In this article
In an age where the digital realm plays an ever-increasing role in our lives, the safeguarding of sensitive information has never been more critical. This is where the ISMS, or Information Security Management System, steps into the limelight. An ISMS is more than a framework; it’s a shield that organizations wield to protect their data from an array of threats, ensuring that information remains secure, confidential, and accessible only to those who should have it. This article is your gateway to understanding ISMS, its significance, its components, and how it’s become an essential part of modern information security.
Unraveling the Essence of an ISMS
At its core, an Information Security Management System (ISMS) is a comprehensive framework designed to manage and protect an organization’s sensitive information. This includes any data, whether digital or physical, that holds value and significance for the organization. The primary goal of an ISMS is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of this information while managing associated risks effectively.
The concept of an ISMS may seem complex, but at its heart, it is a structured approach that empowers organizations to mitigate the risks and vulnerabilities associated with information security. It’s about creating a culture of security, implementing robust controls, and providing assurance that sensitive information remains safe from a multitude of threats.
The key aspects of an ISMS
An effective ISMS comprises several essential components that work in concert to protect an organization’s information. Here are the key building blocks:
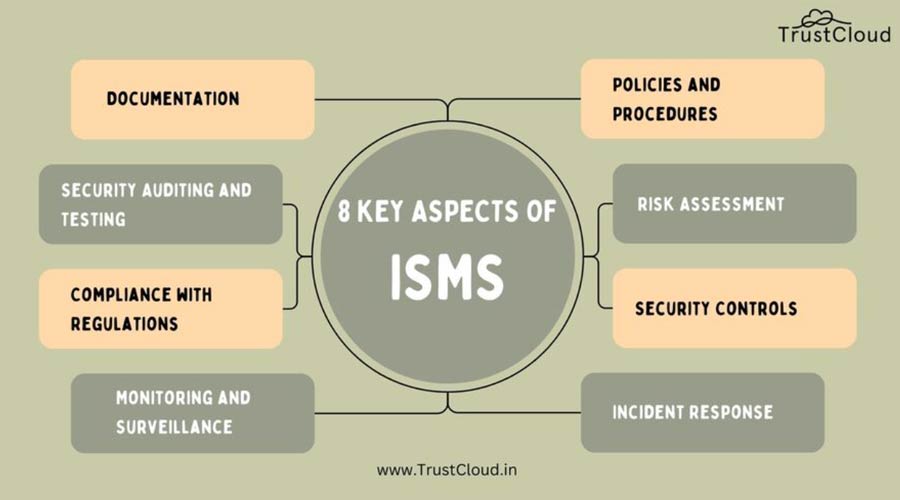
- Policies and Procedures: Establishing information security policies and procedures that outline the organization’s commitment to safeguarding information assets, as well as specific security measures and guidelines,
- Risk Assessment: Identifying and assessing information security risks, including potential threats and vulnerabilities, and determining the impact of security incidents
- Security Controls: It is about implementing a range of security controls and safeguards to protect information assets. These controls can include encryption, access control, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and more.
- Incident Response: Developing plans and procedures for responding to security incidents, breaches, and data breaches to minimize damage and ensure regulatory compliance
- Monitoring and Surveillance: Continuously monitoring and reviewing the organization’s information security posture, including the use of security tools and technologies to detect and respond to threats.
- Compliance with Regulations: It helps ensure that the organization complies with relevant information security laws, regulations, and standards; this may include standards like ISO 27001 or regulatory requirements specific to an industry.
- Security Auditing and Testing: Conducting regular security audits, vulnerability assessments, and penetration testing to evaluate the effectiveness of security controls and identify areas that need improvement
- Documentation and Record-Keeping: Maintaining records and documentation related to information security policies, risk assessments, security incidents, and compliance efforts
The Importance of ISMS: Safeguarding Information in a Digital Age
In the fast-paced and interconnected digital landscape of today, the importance of Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) cannot be overstated. ISMS serves as a robust framework designed to safeguard sensitive information, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of data within an organization. Let’s delve into the key aspects that highlight the significance of ISMS.
- Protection of Sensitive Information: ISMS is crucial for protecting sensitive information within an organization. By implementing robust security measures, access controls, and encryption, ISMS ensures the confidentiality of critical data, safeguarding it from unauthorized access or disclosure. This protection extends to sensitive customer information, intellectual property, and other confidential assets.
- Risk Management and Mitigation: One of the primary importances of ISMS is its role in risk management. ISMS allows organizations to identify, assess, and mitigate risks related to information security. By understanding potential threats and vulnerabilities, organizations can implement appropriate controls and measures to minimize the impact of risks, contributing to the overall resilience of the business.
- Regulatory Compliance: In today’s regulatory environment, adherence to laws and standards is paramount. ISMS provides a structured framework for organizations to align their information security practices with regulatory requirements. Compliance with data protection laws, industry standards, and other regulations is not only a legal necessity but also enhances the organization’s reputation and trustworthiness.
- Business Continuity and Resilience: ISMS contributes significantly to business continuity and resilience. By identifying and addressing potential disruptions to information systems, organizations can ensure the availability and functionality of essential processes. This resilience is vital for maintaining operations during unexpected events, such as cyberattacks or natural disasters, minimizing downtime and financial losses.
- Enhanced Customer Trust and Reputation: Building and maintaining customer trust is a critical aspect of business success. ISMS plays a pivotal role in this by ensuring the secure handling of customer data. When customers are confident that their information is protected, it strengthens their trust in the organization. This, in turn, enhances the organization’s reputation, fostering long-term relationships with clients, partners, and stakeholders.
Implementing an ISMS
Implementing it is not a one-size-fits-all endeavor. It requires careful planning, customization, and ongoing commitment. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Define Objective:
Begin by defining the objectives of your ISMS. What information do you need to protect, and what are the specific risks and threats you face? - Risk Assessment
Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential vulnerabilities and threats to your information. This will guide your security measures. - Security Controls
Select and implement security controls that align with your identified risks and objectives. These can include technical measures, policies, and procedures. - Training and Awareness
Train your employees and create awareness.
The ISO 27001 standard is one of the most well-known and widely used frameworks for implementing an ISMS. It provides a systematic and comprehensive approach to information security management and is recognized internationally. Implementing it is crucial for organizations, especially in an era where cyber threats and data breaches are prevalent. It helps organizations protect their sensitive information, maintain the trust of customers and stakeholders, and avoid the potential legal and financial consequences of security breaches.
Read more Compliance & Cybersecurity Articles from TrustCloud.
