Host hardening documentation: a comprehensive guide
Host hardening documentation is a critical component of this process, serving as the blueprint for securing your servers and workstations. In the dynamic landscape of cybersecurity, the protection of your organization’s digital assets is paramount. One fundamental aspect of safeguarding your systems is host hardening. In this article, we will unravel the concept of host hardening documentation, exploring what it is, why it matters, and how to create an effective document to fortify your IT infrastructure.
What is host hardening?
Host hardening refers to the process of enhancing the security of a computer system by reducing its attack surface. This involves configuring a host, whether it’s a server or a personal computer, to eliminate vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. These vulnerabilities often stem from default configurations, unnecessary services, or software vulnerabilities, and they can provide an entry point for cyberattacks.
Host hardening typically involves the following key steps:
- Disabling Unnecessary Services: Reducing the number of running services and applications on a host decreases the potential attack vectors.
- Patching and Updating: Regularly updating the operating system and software applications to fix known vulnerabilities
- Access Control: Implementing strict user access controls and ensuring strong password policies
- Firewall Configuration: Setting up a robust firewall to filter network traffic and block unwanted connections
- File and Directory Permissions: Adjusting file and directory permissions to limit unauthorized access
- Monitoring and Logging: Implementing monitoring and logging to detect and respond to security incidents
What is host hardening documentation?
Host-hardening documentation is a structured set of guidelines and procedures that organizations use to secure their hosts effectively. This documentation is a reference point for system administrators, IT staff, and security teams to follow in order to ensure a consistent, secure configuration of all hosts in an organization.
Host hardening documentation typically refers to a set of guidelines, procedures, and best practices aimed at securing and enhancing the resilience of computer systems, servers, or network devices. Here’s a basic outline of what such documentation might include:
- Introduction: Provide an overview of the purpose and importance of host hardening, emphasizing the need to protect against various cybersecurity threats and vulnerabilities.
- Scope and Objectives: Define the scope of the host hardening process, specifying which systems or devices are covered and outlining the objectives of the hardening effort, such as reducing the attack surface, enhancing security posture, and ensuring compliance with relevant standards or regulations.
- Baseline Configuration: Document the initial configuration settings for the host system or device, including operating system (OS) settings, network configurations, user accounts and permissions, and installed software.
- Security Policies and Guidelines: Outline the security policies, standards, and guidelines that govern the host hardening process. This may include password policies, encryption requirements, firewall configurations, and access control measures.
- Hardening Procedures: Provide step-by-step instructions for implementing specific hardening measures and security controls. This may involve disabling unnecessary services, applying software patches and updates, configuring security features such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems, and implementing security-enhancing technologies like encryption and multi-factor authentication.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Describe procedures for monitoring the effectiveness of host hardening measures, such as conducting regular security assessments, vulnerability scans, and penetration tests. Also, outline ongoing maintenance tasks, such as applying security patches and updates, reviewing and updating configurations, and monitoring system logs for suspicious activity.
- Compliance and Reporting: Specify any regulatory or compliance requirements that the host hardening process must adhere to, such as HIPAA, GDPR, or industry-specific standards like PCI DSS. Also, outline reporting requirements for documenting compliance with security policies and standards.
- References and Resources: Provide references to relevant documentation, tools, and resources that can assist in the host hardening process, such as security configuration guides, vendor documentation, and online forums or communities.
By documenting host hardening procedures in a structured and comprehensive manner, organizations can effectively mitigate security risks and strengthen the overall security posture of their IT infrastructure.
Here are the key components of host hardening documentation:
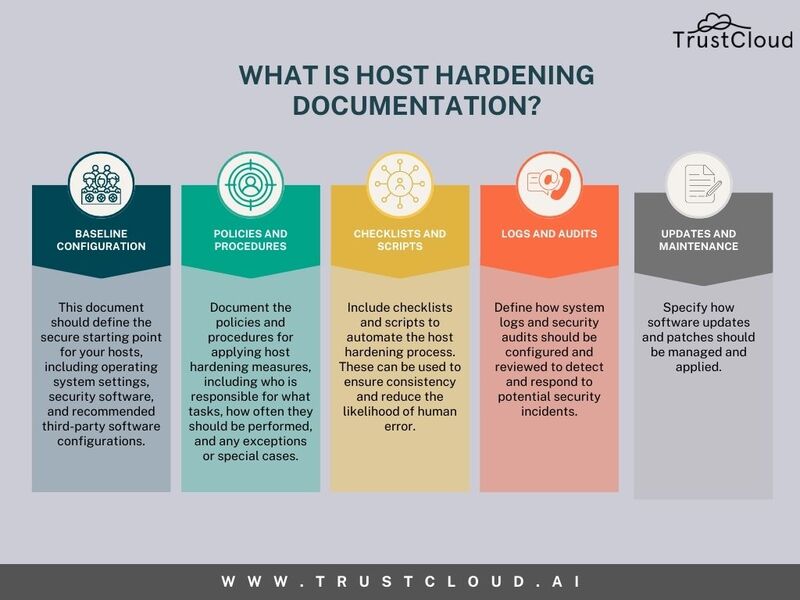
Why is it important?
Host-hardening documentation plays a pivotal role in enhancing your organization’s cybersecurity posture for several reasons:
- Consistency: It ensures that all hosts within your organization adhere to the same security standards, reducing the risk of overlooked vulnerabilities.
- Efficiency: By providing clear, step-by-step instructions, host hardening documentation simplifies the process of securing hosts, saving time and resources.
- Compliance: Many industries and regulatory bodies require organizations to maintain secure configurations, making host hardening documentation essential for compliance.
- Scalability: As your organization grows, host hardening documentation can be scaled to accommodate new hosts and technologies.
Common vulnerabilities and threats to hosts
Hosts face a myriad of vulnerabilities and threats, each capable of compromising the security of your systems. One common vulnerability is outdated software. Software vendors frequently release updates to patch security holes, but without diligent application of these updates, systems remain exposed to known exploits.
Another vulnerability comes from unnecessary services running on the host. Each service increases the attack surface, providing potential entry points for attackers. Services such as remote access protocols, if not securely configured or left running when not needed, can be exploited by attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Moreover, weak authentication mechanisms present a substantial threat. Simple or default passwords can easily be guessed or cracked by attackers using brute force methods. Similarly, the lack of multi-factor authentication (MFA) can make it easier for unauthorized users to gain access if they obtain a user’s credentials.
Creating effective host hardening documentation
To create effective host hardening documentation, consider the following tips:
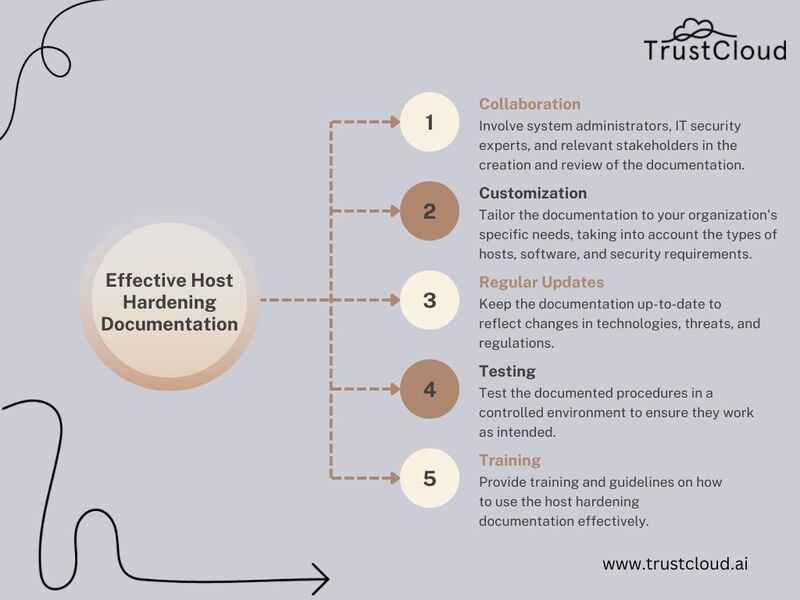
Host hardening documentation is an indispensable tool in your organization’s cybersecurity toolkit. It provides the guidance and structure needed to secure your hosts, mitigate vulnerabilities, and bolster your defenses against cyber threats. By creating and maintaining comprehensive documentation, you’re taking a proactive step towards safeguarding your digital assets and maintaining the trust of your clients, partners, and stakeholders in an increasingly interconnected world.
Why is host hardening documentation requested during audits?
In the world of information security and compliance, audits are essential processes that organizations undergo to ensure they are meeting the required standards and adhering to best practices. One recurring request that often comes up during these audits is the submission of host hardening documentation. But why is host hardening documentation such a crucial component of audits, and what makes it so important? In this section, we’ll explore the reasons behind the demand for host hardening documentation in audits.
Host hardening documentation is a fundamental requirement during audits for several critical reasons. First and foremost, it serves as a tangible demonstration of an organization’s commitment to information security. Auditors look for evidence that an organization has taken proactive measures to secure its host systems and mitigate potential vulnerabilities. Host hardening documentation offers a structured overview of the security measures in place, configurations, and best practices followed. It ensures that the organization has implemented robust security controls and diligently worked towards reducing its attack surface, ultimately reinforcing the integrity of sensitive data.
Furthermore, it plays a pivotal role in verifying compliance with industry-specific regulations and standards. Numerous regulatory frameworks, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and GDPR, mandate that organizations maintain secure configurations on their systems to protect sensitive information. During audits, presenting comprehensive documentation is crucial for demonstrating adherence to these regulations. It offers auditors a clear view of how security standards are implemented and adhered to, helping organizations avoid costly penalties and reputational damage resulting from compliance violations.
It also aids auditors in vulnerability assessment. Auditors need to assess the security posture of an organization’s IT infrastructure, and this documentation is the starting point for such assessments. By analyzing the documentation, auditors can identify potential vulnerabilities, assess their impact, and make recommendations for improvements. This assessment ensures that the organization’s hosts are not only secure but also actively monitored and assessed for security weaknesses, contributing to a more robust security posture and reducing the risk of security breaches.
Tools and resources for host hardening
A variety of tools and resources are available to assist in the host hardening process. Security benchmarks and guidelines, such as those provided by the Center for Internet Security (CIS), offer valuable insights into securing various systems. These benchmarks provide detailed recommendations for hardening specific operating systems and applications.
Security scanning tools also play a crucial role in host hardening. Tools like Nessus or OpenVAS can scan your systems for known vulnerabilities, providing a detailed report of potential weaknesses. These tools help identify areas that require attention and can guide the hardening process.
In addition, configuration management tools such as Ansible, Chef, or Puppet can automate the application of hardening measures across multiple systems. These tools can enforce desired configurations, ensuring that all systems adhere to your hardening standards consistently and efficiently.
Conclusion
Host hardening is a critical component of cybersecurity, essential for protecting your systems against evolving threats. By understanding and applying the principles of host hardening, you can significantly enhance the security of your digital assets. Remember, host hardening is an ongoing process, requiring continuous effort and vigilance to maintain system security.
Implementing comprehensive documentation, adhering to best practices, utilizing available tools and resources, and staying informed about new threats are all crucial for effective host hardening. By taking these steps, you can ensure that your systems are well-protected, safeguarding your information and assets against unauthorized access and cyberattacks.
In summary, host hardening documentation is an essential tool in demonstrating an organization’s commitment to security, ensuring compliance with regulations, and aiding in vulnerability assessments, making it a central request during audits.
Want to learn more about GRC?
Explore our GRC launchpad to gain expertise on numerous compliance standards and topics.
Join our TrustCommunity to learn about security, privacy, governance, risk and compliance, collaborate with your peers, and share and review the trust posture of companies that value trust and transparency!
Want to see how to turn GRC into a profit center?
Ready to save time and money on audits, pass security reviews faster, and manage enterprise-wide risk? Let’s talk!



